
How Astrakode’s Private Blockchain Solution Helped Systema S.r.l. Improve Document Security and Privacy
Sharing documents is a common practice in business, but the advent of blockchain technology has…
Welcome to the exciting world of blockchain! If you’ve ever wondered what this revolutionary technology is all about, you’ve come to the right place. In this beginner’s guide, we aim to demystify the concept of blockchain, break it down into simple terms, and help you understand its core components. Whether you’re a curious individual, a tech enthusiast, or an entrepreneur looking to explore the potential of this transformative technology, this guide will provide a solid foundation for grasping the basics of blockchain.
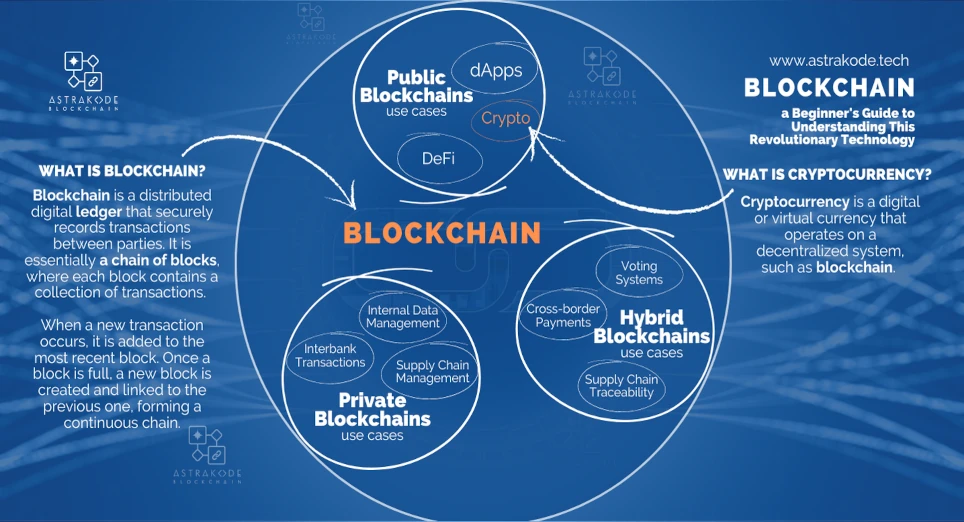
So, what exactly is blockchain? In simple terms, a blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that securely records transactions between parties. It is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a collection of transactions. When a new transaction occurs, it is added to the most recent block. Once a block is full, a new block is created and linked to the previous one, forming a continuous chain.
Now, let’s dive into the core components of a blockchain:
One of the key aspects of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single authority controls the flow of information or assets, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network with no central authority. This means that every participant in the network has a copy of the entire blockchain, and each copy is updated simultaneously whenever a new transaction is added.
This decentralized approach offers several benefits:
By understanding the core components and decentralized nature of blockchain, you can begin to appreciate the potential of this revolutionary technology to transform various industries and reshape the way we conduct transactions in the digital world.
The blockchain landscape is brimming with opportunities, especially considering the diverse types available: public, private, and hybrid. Each offers distinct benefits, tailored solutions, and transformative potential for various industries and daily life. Let’s explore these blockchain varieties together.
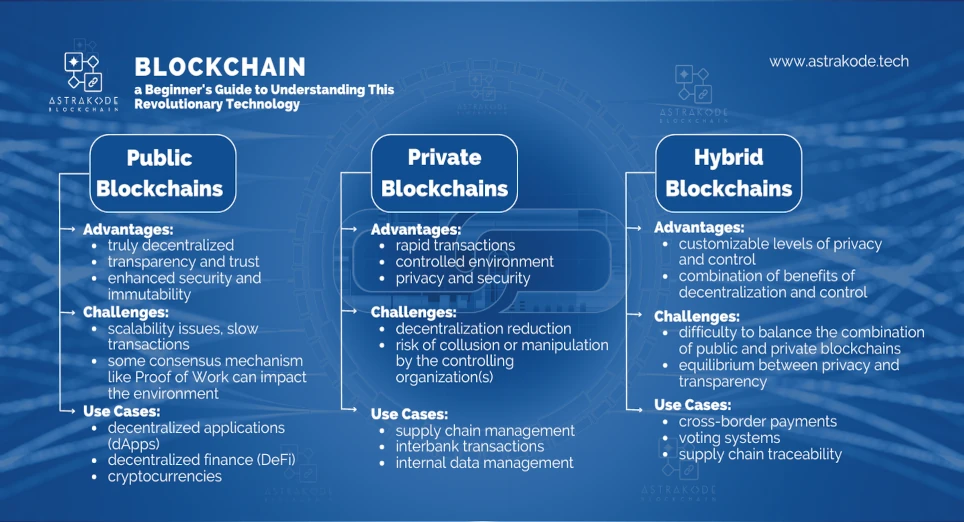
Public blockchains, often called permissionless blockchains, open their doors to everyone, inviting participants from all walks of life to join the network. This inclusive approach fosters decentralization and transparency, as anyone can read, write, and audit transactions without requiring special permissions. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public blockchains that have captivated the world.
Advantages:
Challenges:
Use cases: From decentralized applications (DApps) to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and cryptocurrencies, public blockchains are the foundation for numerous innovations.
Private blockchains, or permissioned blockchains, cater to a select group of participants who have been granted access to the network. Often governed by a single organization or a consortium, private blockchains offer a more controlled environment ideal for internal business purposes.
Advantages:
Challenges:
Use cases: From supply chain management to interbank transactions and internal data management, private blockchains provide secure and efficient solutions for businesses. Check out how we actually helped one of our customer Systema S.r.l.
Hybrid blockchains merge the strengths of public and private blockchains, creating a flexible and adaptable solution. In a hybrid blockchain, certain aspects of the network are open to everyone, while others are restricted to authorized participants. This enables organizations to enjoy the transparency and security of public blockchains while maintaining control over sensitive data.
Advantages:
Challenges:
Use cases: Hybrid blockchains are poised to revolutionize industries such as cross-border payments, voting systems, and supply chain traceability.
While cryptocurrencies and blockchain are often mentioned together, it’s essential to understand that they are not the same thing. Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and operates on a decentralized system, such as blockchain. On the other hand, blockchain is the underlying technology that enables the existence of cryptocurrencies and has numerous other applications beyond digital currencies. Let’s dive deeper into the relationship between these two concepts and the distinctions between them.
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are perhaps the most well-known applications of blockchain technology. Operating on a decentralized network, these digital currencies utilize blockchain to securely record and verify transactions, eliminating the need for a central authority like a bank or government. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies offers increased security, transparency, and reduced transaction costs compared to traditional financial systems.
However, it’s crucial to remember that cryptocurrencies are just one example of how blockchain technology can be utilized. Blockchain’s potential extends far beyond digital currencies and has the capacity to transform various industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and voting systems, among others.
As we continue our exploration of blockchain technology, we’ll now delve into the world of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). These innovative concepts are transforming the way we think about digital agreements and applications, offering new possibilities for automating processes and creating truly decentralized solutions.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Similar to digital vending machines, smart contracts operate by meeting predefined conditions. Just as users insert money and make selections to acquire desired items, **likewise**, smart contracts automatically execute predetermined actions when specific criteria are met, streamlining transactions without intermediaries.
These digital agreements run on the blockchain, allowing them to be secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. The most significant advantage of smart contracts is that they automatically execute and enforce the terms of a contract once the specified conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the potential for disputes.
Smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize various industries, from finance and real estate to supply chain management and insurance. By automating processes and removing intermediaries, smart contracts can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance trust between parties.
DApps are applications that run on a decentralized network, like a blockchain, instead of a centralized server. By leveraging the power of blockchain technology, DApps can offer users increased security, transparency, and control over their data.
DApps have the potential to disrupt various sectors, including finance, gaming, content sharing, and social media. Some of the most promising use cases for DApps include decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
As we’ve seen throughout this guide, blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, such as:
However, there are also challenges to consider:
Despite these challenges, it’s undeniable that blockchain technology holds vast potential, and industries have only scratched the surface of exploring its applications. With optimism and determination, we can overcome these hurdles and harness the power of blockchain to create a more secure, transparent, and decentralized digital future.
AstraKode Blockchain acknowledges the challenges faced by businesses when adopting blockchain technology, such as complexity, stack size, and scalability. By offering a low code solution that is user-friendly and tailored for all sizes of businesses, We aim to simplify the process and provide the necessary resources to help companies unlock new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. Sign up now and join.
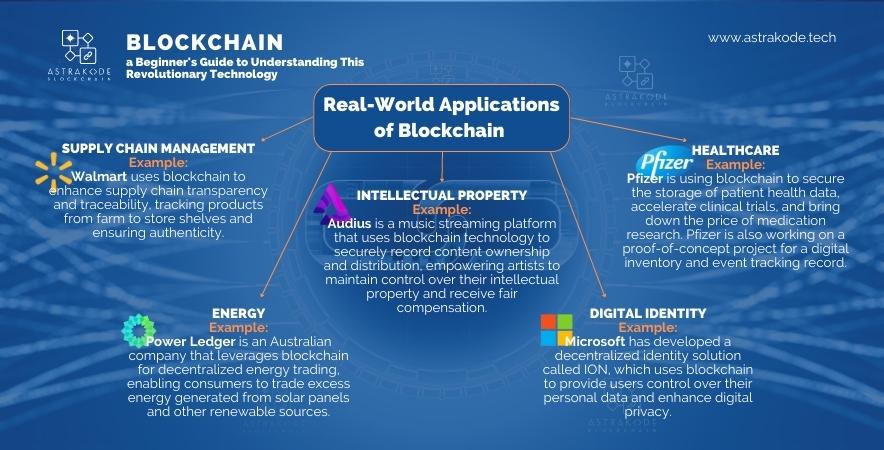
The potential of blockchain technology stretches far beyond cryptocurrencies, with numerous real-world applications emerging across various industries. In this section, we’ll explore some of these exciting use cases that are transforming the way we conduct business, manage assets, and interact with technology.
These real-world applications are just the beginning, highlighting blockchain’s potential to transform industries and enhance our lives. As we explore new use cases, the future of blockchain technology holds endless promise.
AstraKode Blockchain transforms business and developer engagement with blockchain by offering a user-friendly, low-code web based platform. Its intuitive network composer, smart contract IDE, and visual environment empower users of all skill levels to easily create and deploy blockchain applications. You don’t need to be a developer to explore the blockchain world. By familiarizing yourself with blockchain, and taking some time to understand the platform, you can hop on this revolutionary technology.
Getting started with AstraKode Blockchain is a simple and straightforward process. Sign up for an account and explore the platform’s dashboard to discover its powerful features. Create a new project, design your network using the visual composer, and develop smart contracts with the low-code IDE. Test your application to ensure its functionality and performance; subsequently, deploy it to the AstraKode Blockchain network. Monitor your project’s performance and leverage the supportive community for assistance and collaboration. With AstraKode, you will have the capability to effortlessly create innovative blockchain solutions.
Throughout this article, we’ve taken an exciting journey into the world of blockchain, shedding light on its core components and decentralized nature. We’ve also seen how it goes beyond cryptocurrencies, touching various aspects of our lives and different industries. We’ve explored blockchains, smart contracts, and decentralized applications, revealing their potential to revolutionize digital interactions.
AstraKode Blockchain is here to make blockchain more accessible and welcoming for everyone, from businesses to developers and curious individuals. With its user-friendly, low-code platform, AstraKode is a fantastic companion on your adventure into the world of blockchain, providing a seamless gateway to innovate and explore new possibilities. Sign up here and start exploring!

Sharing documents is a common practice in business, but the advent of blockchain technology has…

Blockchain technology has taken the world by storm and has become a vital tool in…

Blockchain technology is changing the world, and it’s no secret that blockchain developers are in…